The Sanyo MPC-11 or Wavy 11
The MPC-11 offered more RAM than it's predecessors, the computer came with 64kByte, which allowed the computer to run a broader range of software. The keyboard is a full-size keyboard making prolonged typing much more comfortable. This model solidified Sanyo's reputation for providing reliable and versatile MSX1 computers for both home and educational markets.
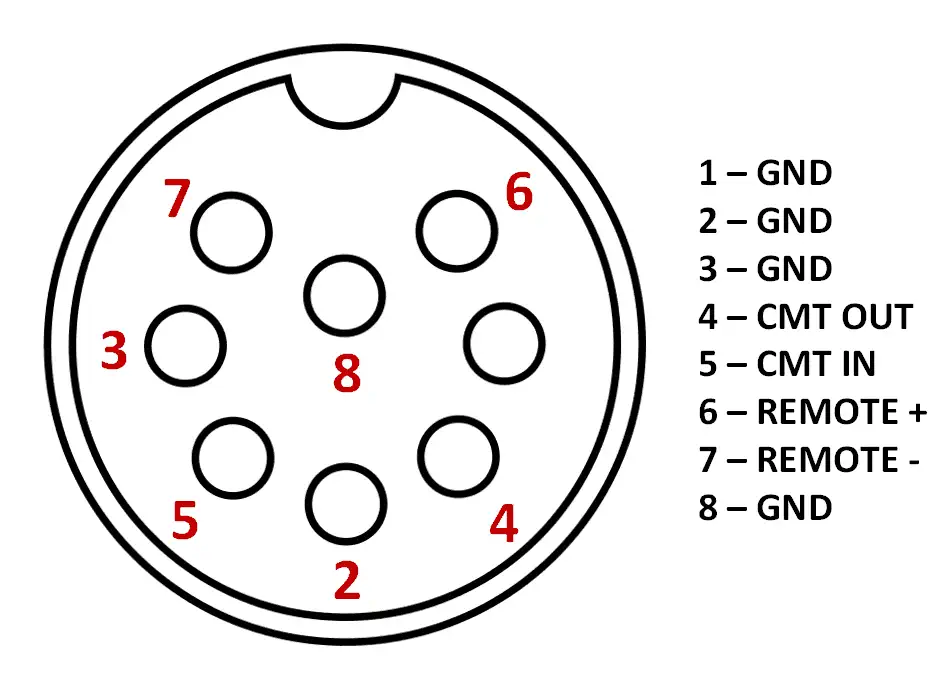
MSX Cassette Pin Layout
The MSX Standard calls for all MSX computers to have a standard data-cassette port. This port transports the audio-in/out signals to and from the datarecorder and the computer has a relay-switch on board to turn the recorder on and off.
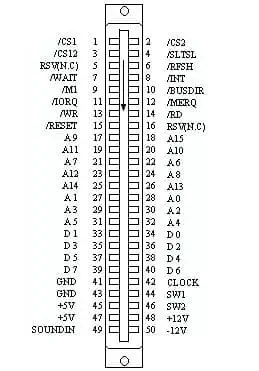
MSX Cartridge Connector
The MSX Cartridge system uses a 50-pin flat-edge connector to connect to the systems expansion bus. The cartridge slot maps into one of the main- or sub-slots.
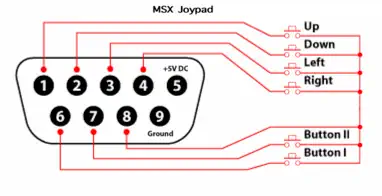
MSX Joystick Connector
TMS9918 Series Video Display Processor (99n8, 99n9, 91n8, 91n9)
The TMS9918 is a series of video display controllers (VDC) manufactured in 1979 by Texas Instruments, also refered to as 'Video Display Processor' (VDP). The TMS9918 and its variants were used in the ColecoVision, CreatiVision, Memotech MTX, MSX, NABU Personal Computer, SG-1000/SC-3000, Spectravideo SV-318, Spectravideo SV-328, Sord M5, Tatung Einstein, Texas Instruments TI-99/4, Casio PV-2000, Coleco Adam, Hanimex Pencil II, and Tomy Tutor.
Key Features:
- 256x192 pattern based color pixels per screen
- 16 different colors
- 8-bit memory mapped CPU interface
- No need for DMA, CPU can access VRAM
- 32 single color Sprites per screen (4 per scanline)
Variants:
- TMS9918A - 60Hz output, NTSC video
- TMS9928A - 60Hz output, YPbPr video
- TMS9929A - 50Hz output, YPbPr video
- TMS9118 - Different RAM than TMS9918A, otherwise identical
- TMS9128 - Different RAM than TMS9928A, otherwise identical
- TMS9129 - Different RAM than TMS9929A, otherwise identical

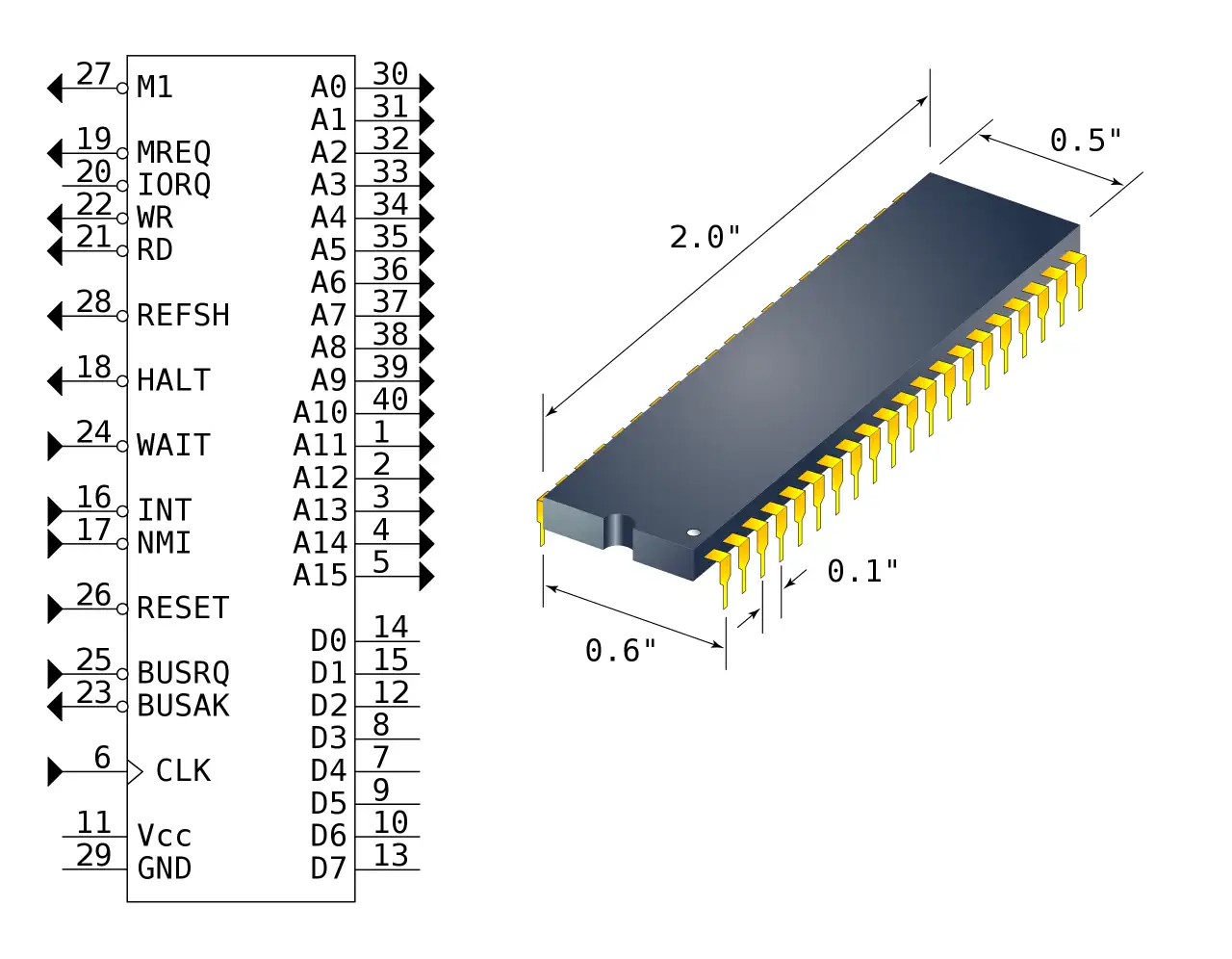
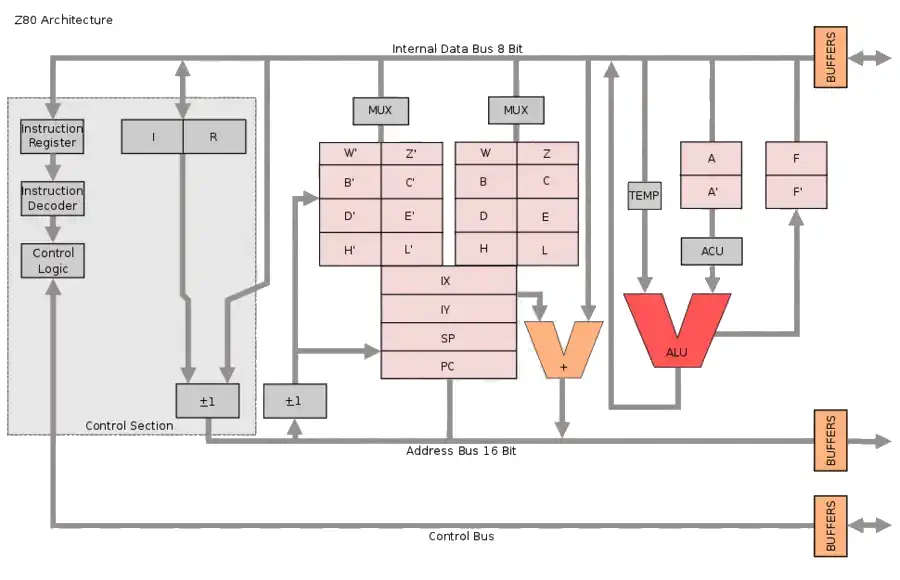
CPU View - Zilog Z80 Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer
VRAM: 16kB Sound Chip General Instruments AY-3-8910 Programmable Sound Generator Sound 3 wave channels + white noise Display Chip Texas Instruments TMS9118NL VDP Display 40x24 text
32x24 16 color text, pattern based
256x192 16 color, 2 color per 8 pix. Best Text 40x24 Best Color 16 colors (2 per 8 pixels) Graphics 256x192 in 16 colors Sprites 1 color, 16x16, 4/scanline, 32 total System OS MSX 1 BIOS / MSX BASIC Storage External Tape, ROM cartridges Original Price ¥99,800

