Sega Game Gear
SEGA’s first foray into the portable gaming market and a direct competitor to Nintendo’s Game Boy. Released on October 6th 1990 in Japan and April 26th 1991 in America and Europe. It was later re-released by Majesco in 2000 but only in America. The console’s main selling point was it’s full color, backlit display.
The Game Gear is architecturally very similar to the Master System but with a broader color palette. Master System games can actually be played on the Game Gear with use of an adapter. The console’s biggest drawback is its need for 6 AA batteries to run without a power adapter. It suffers from poor battery life and the capacitors have a tendency to leak and cause the screen to fade and the sound to quieten over time.
A total of 390 games were released for the system and 10.62 million consoles were sold worldwide by March 1996.
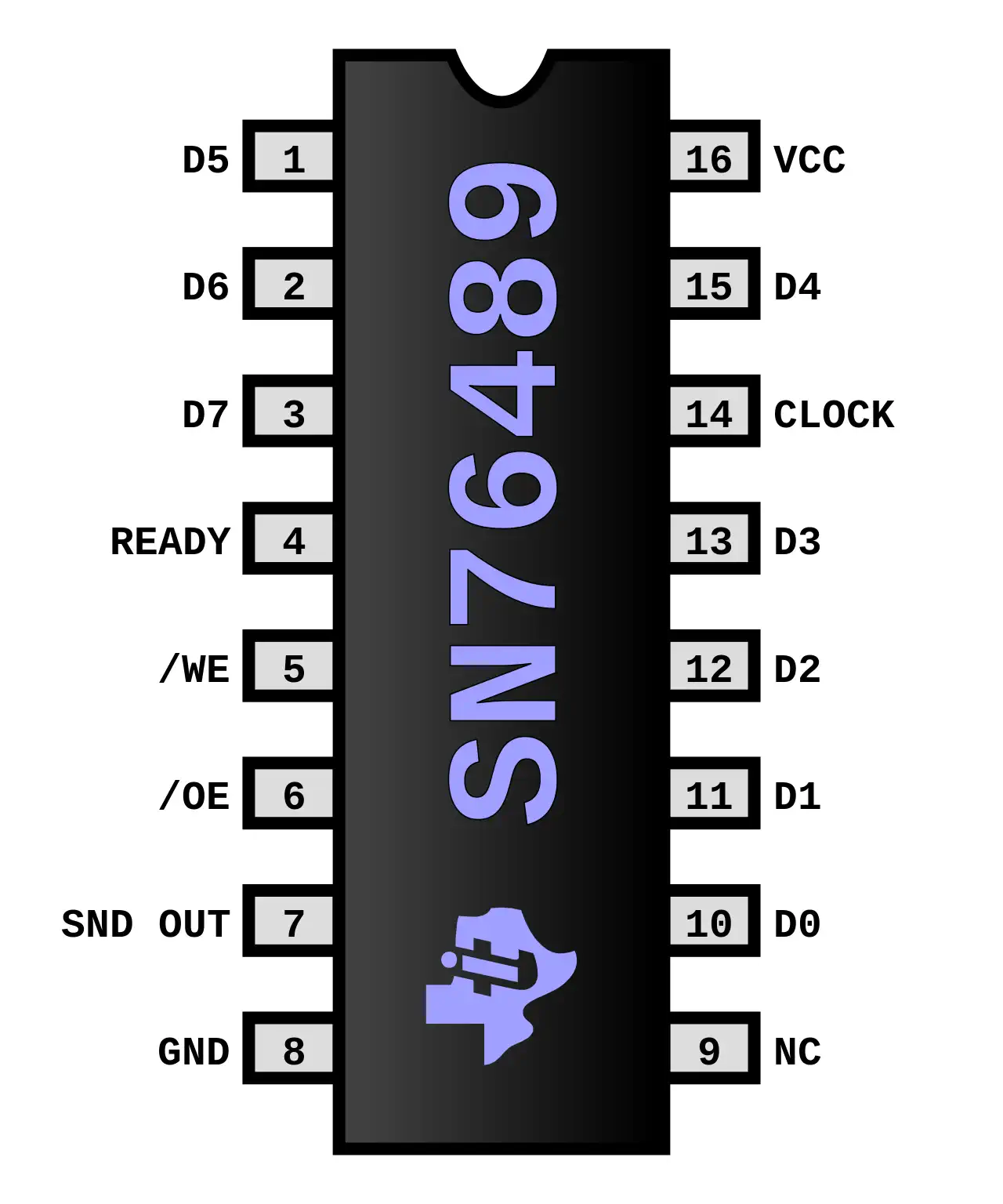
Texas Instruments SN76489 Sound Generator
The SN76489 Digital Complex Sound Generator (DCSG) is a TTL compatible programmable sound generator chip created by Texas Instruments. It main application was the generation of music and sound effects in home computers, arcade machines and home game consoles. Functionally the chip was similar to the General Instrument AY-3-8910.
Sound Capabilities:
- 3 Square Wave tone generators, 16 volume levels
- 1 White Noise Generator (white and periodic noice, 3 frequencies, 16 volumes)
The SN76489 Was originally designed to be used in the TI-99/4 computer, where it was first called the TMS9919 and later SN94624, and had a 500 kHz max clock input rate. Later, when it was sold outside of TI, it was renamed the SN76489, and a divide-by-8 was added to its clock input, increasing the max clock input rate to 4 MHz, to facilitate sharing a crystal for both NTSC colorburst and clocking the sound chip. A version of the chip without the divide-by-8 input was also sold outside of TI a
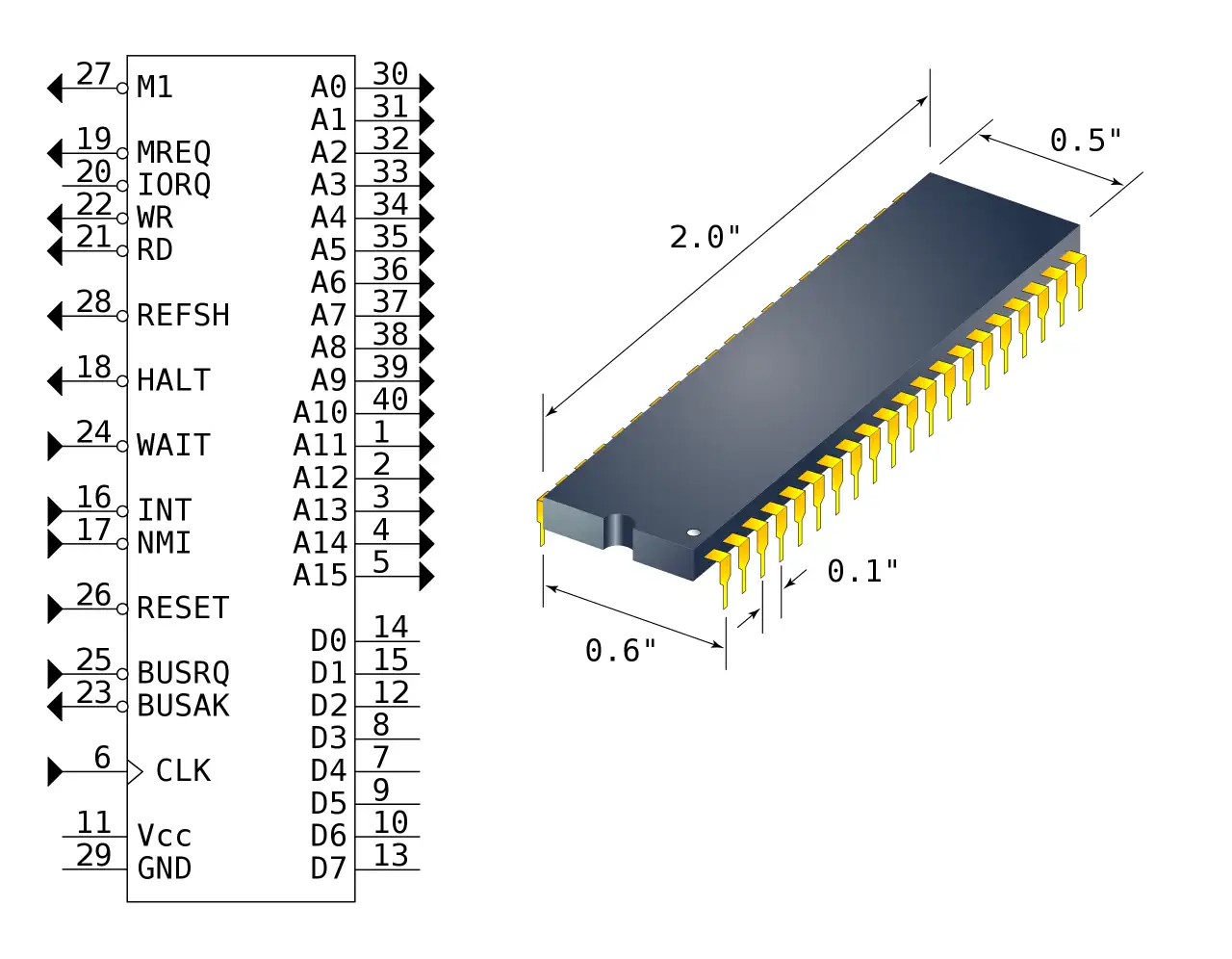
CPU View - Zilog Z80 Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer
VRAM: 16kB Sound Chip SN76489 PSG (built into VDP), YM2413 FM Sound PSG: 3 Square waves, 1 noise generator
OPL2 FM Synthesizer Display Chip Sega System 2 custom VDP Display 256x192 in 32 Colors Best Color 32 colors out of 4096 Graphics 160x144 Sprites 64 8x8 sprites in 16 colors. Storage ROM Cartridges

