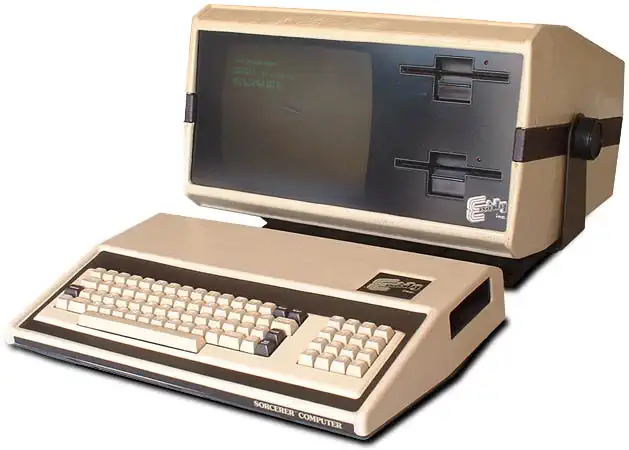
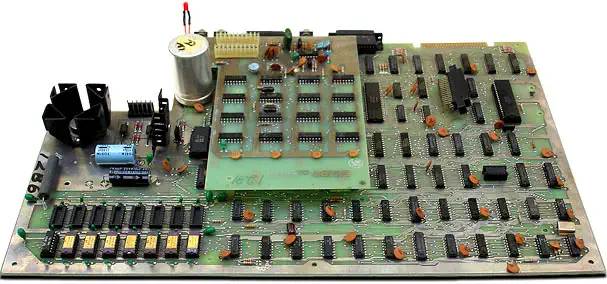
The Exidy Sorcerer
The Exidy Sorcerer was one of the earliest Home Computers, it was launched in 1978. Compared to the competition, the machine had better graphics capability and memory options. It was based on the Z80 architecture which ran at a modest 2MHz.
The Sorcerer was also one of the first home computers that used ROM cartridges as a means of loading software. The cartridge was designed so that it fit in existing 8-track tape casings, which reduced the manufacturing cost. The Sorcerer came standard with a Microsoft BASIC ROM cartridge.
Despite the fact that the marketing was lacking, the machine sold well in Europe. In the Netherlands, the educational broadcasting company TELEAC decided to launch a computer course and viewers could purchase the course bundled with a Sorcerer.
In Europe the Sorcerer was distributed by CompuData, which licensed the design for local production in the Netherlands. Compudata produced the Exidy Sorcerer until 1983 and then switched to a machine of their own design, the Tulip computer which was a 8088-based architecture.
Two versions of the Sorcerer were produced, after some reported problems with the RS-232 serial port on the initial machines, a revised machine the Sorcerer II (DP1000-2 motherboard) was produced, replacing it.
Various hobby groups in the Netherlands and Australia developed RAM upgrades, speed upgrade kits, 80-column add-on cards and updated ROMs that replaced the internal monitor boot-loader program.
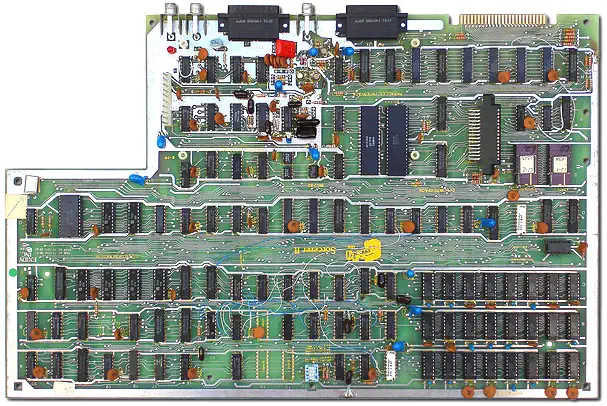
European Model
As the Sorcerer sold better in Europe than in the US, manufacturing was licenced to the CompuData company, which produced a slightly different case for the Exidy, using different colors.
The Exidy Sorcerer
The Exidy Sorcerer was one of the earliest Home Computers, it was launched in 1978. Compared to the competition, the machine had better graphics capability and memory options. It was based on the Z80 architecture which ran at a modest 2MHz.
The Sorcerer was also one of the first home computers that used ROM cartridges as a means of loading software. The cartridge was designed so that it fit in existing 8-track tape casings, which reduced the manufacturing cost. The Sorcerer came standard with a Microsoft BASIC ROM cartridge.
Despite the fact that the marketing was lacking, the machine sold well in Europe. In the Netherlands, the educational broadcasting company TELEAC decided to launch a computer course and viewers could purchase the course bundled with a Sorcerer.
In Europe the Sorcerer was distributed by CompuData, which licensed the design for local production in the Netherlands. Compudata produced the Exidy Sorcerer until 1983 and then switched to a machine of their own design, the Tulip computer which was a 8088-based architecture.
Two versions of the Sorcerer were produced, after some reported problems with the RS-232 serial port on the initial machines, a revised machine the Sorcerer II (DP1000-2 motherboard) was produced, replacing it.
Various hobby groups in the Netherlands and Australia developed RAM upgrades, speed upgrade kits, 80-column add-on cards and updated ROMs that replaced the internal monitor boot-loader program.


Re-used 8-track cartridge shell
The designers of the Exidy Sorcerer used 8-track tape cases as the basis for their catridge design, reducing manufacturing costs.

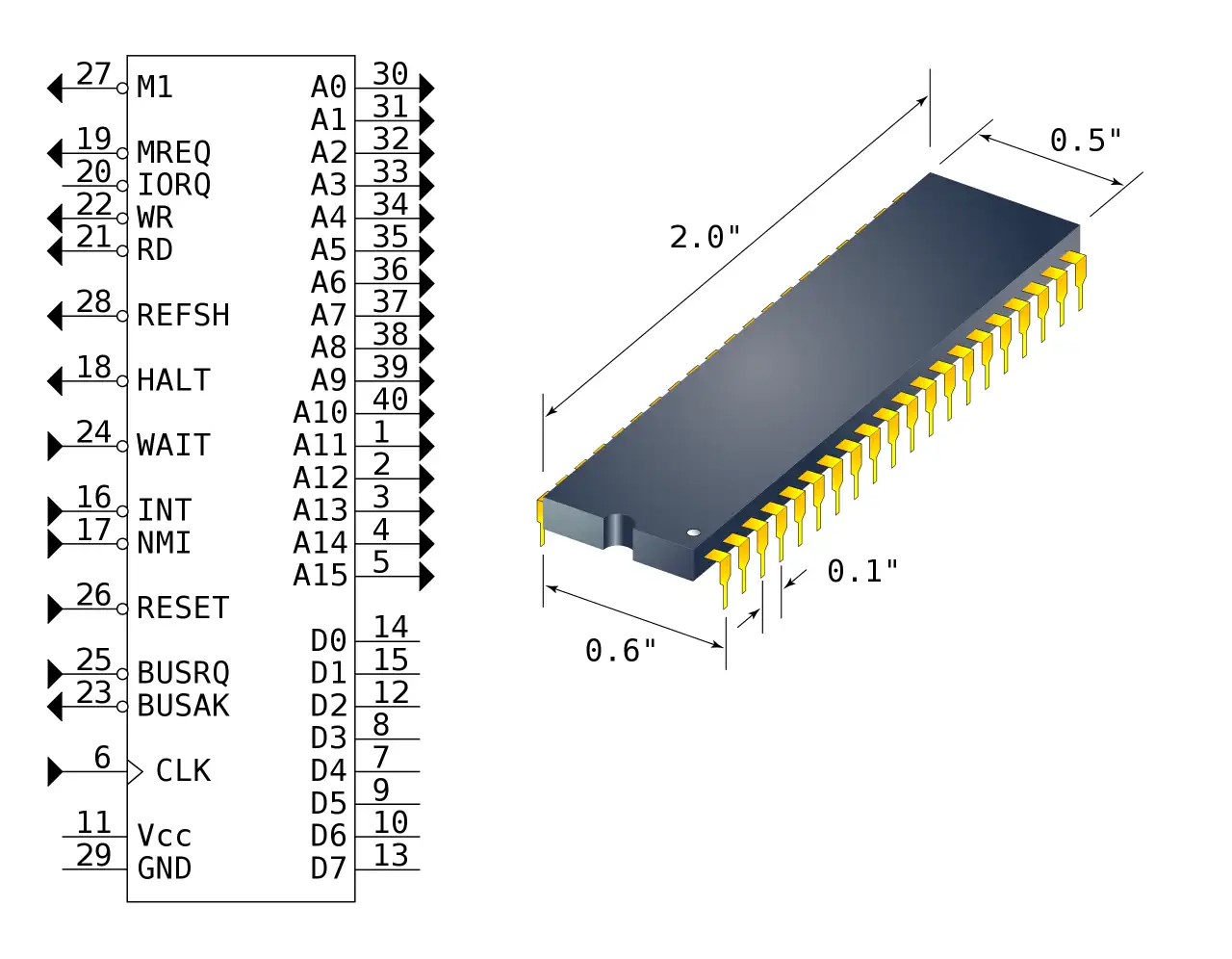
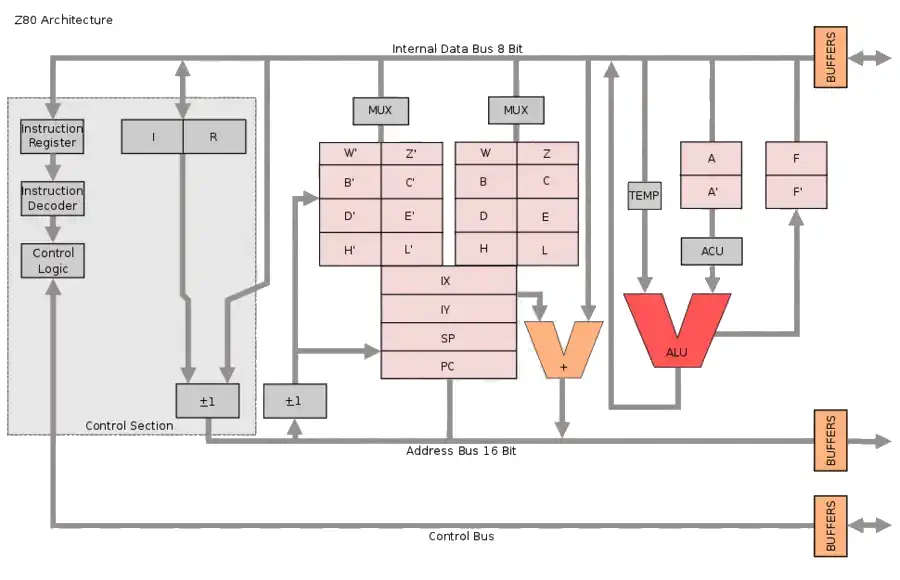
CPU View - Zilog Z80 Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer
RAM max: 32kB Sound Chip none Sound none Display Chip none Display 64x30 text
512x240 Mono Best Text 64x30 Best Color monochrome Graphics 512x240 monochrome Sprites none System OS Monitor System Storage External Tape, ROM cartridges

