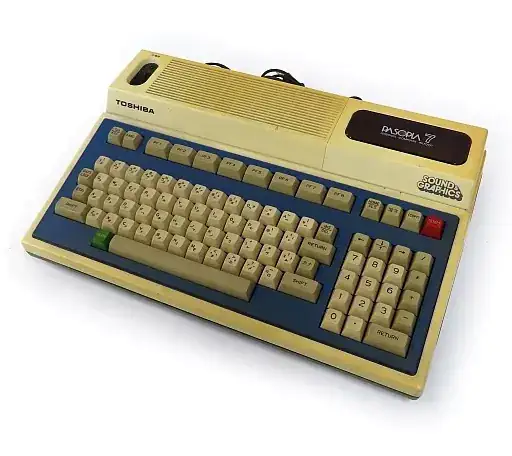
Toshiba Pasopia 7
The Toshiba Pasopia 7 was released in 1983 in Japan. It was the successor of the Pasopia computer, and offered improved sound and graphics. The machine is not fully backwards compatible, but it does support the cartridge type peripherals from the earlier Pasopia.
The computer has a separate VRAM of 48kByte and offered hardware dithering in high resolution mode to simulate intermediate color intensities. The screen uses 640x200 pixels, but each 2 horizontal pixels are combined to produced 27 different colors using the dithering.
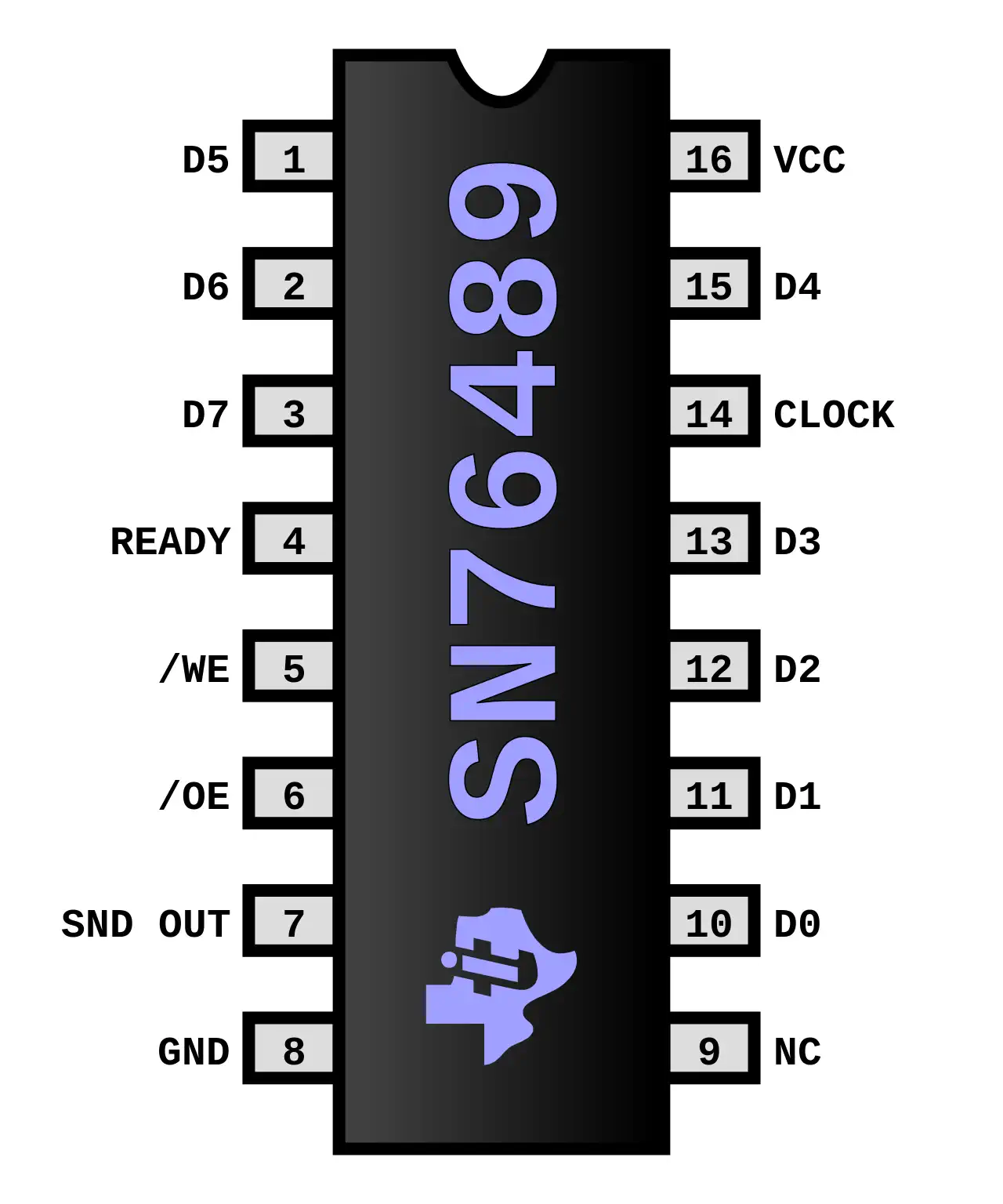
The Pasopia 7 has two SN76489 sound chips to produce six five-octave sound channels, and two noise channels. This was pretty advanced for computers in 1983.
After the release of the Pasopia 7, Toshiba concentrated on producing their Pasopia IQ line of computers, which were all part of the MSX standard, you can find them on Retrobug.org in the MSX group.
Texas Instruments SN76489 Sound Generator
The SN76489 Digital Complex Sound Generator (DCSG) is a TTL compatible programmable sound generator chip created by Texas Instruments. It main application was the generation of music and sound effects in home computers, arcade machines and home game consoles. Functionally the chip was similar to the General Instrument AY-3-8910.
Sound Capabilities:
- 3 Square Wave tone generators, 16 volume levels
- 1 White Noise Generator (white and periodic noice, 3 frequencies, 16 volumes)
The SN76489 Was originally designed to be used in the TI-99/4 computer, where it was first called the TMS9919 and later SN94624, and had a 500 kHz max clock input rate. Later, when it was sold outside of TI, it was renamed the SN76489, and a divide-by-8 was added to its clock input, increasing the max clock input rate to 4 MHz, to facilitate sharing a crystal for both NTSC colorburst and clocking the sound chip. A version of the chip without the divide-by-8 input was also sold outside of TI a
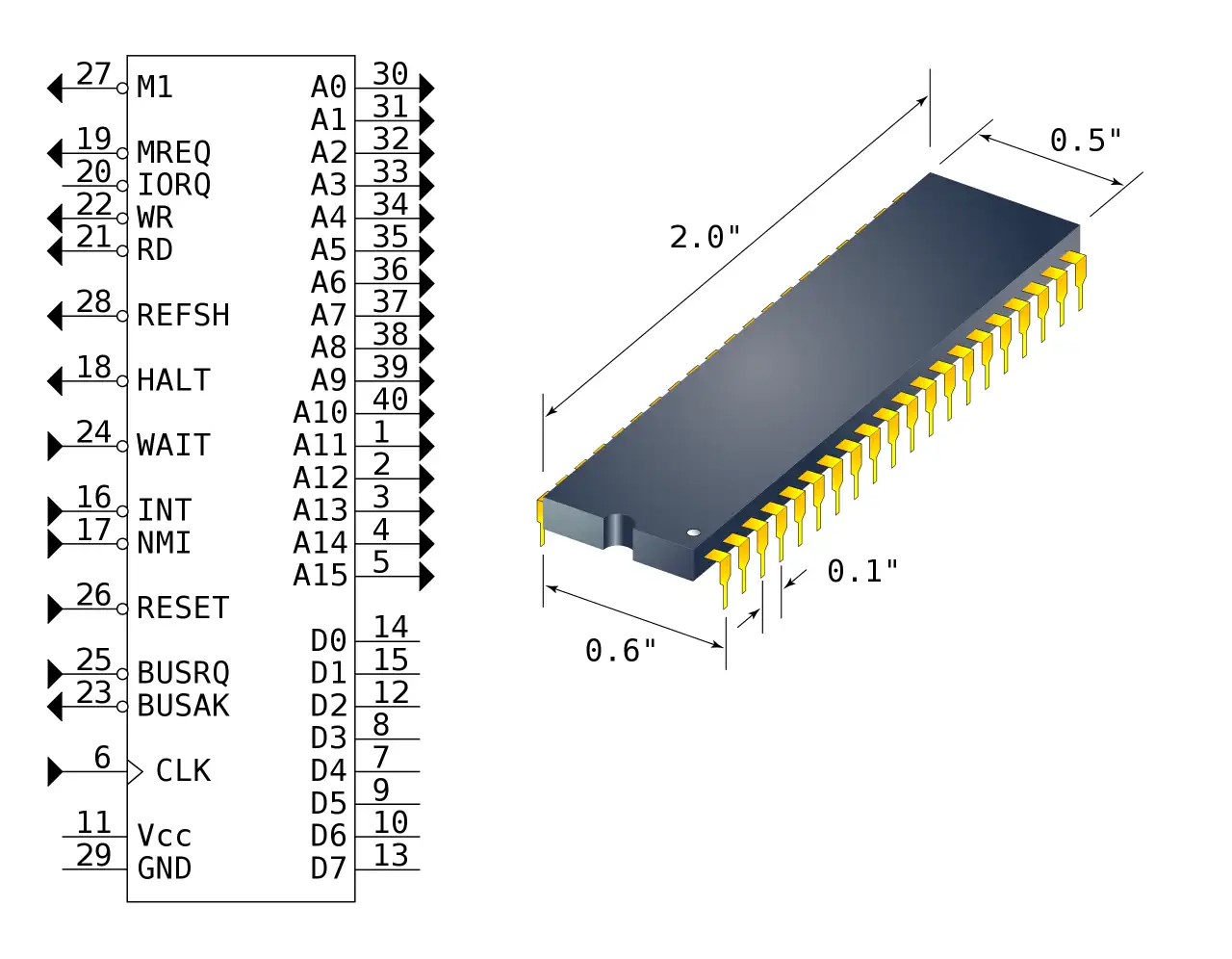
CPU View - Zilog Z80 Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer
ROM: 16kB
VRAM: 48kB Sound Chip 2x Texas Instruments SN79489 Sound 6 Voices, 5 Octaves Display Chip Dedicated dithering circuit Display 320x200
640x200 Best Text 40x24 in 8 base colors Best Color 27 colors, hardware dithering Graphics 640x200 in 8 colors Sprites n/a System OS T-BASIC 7

